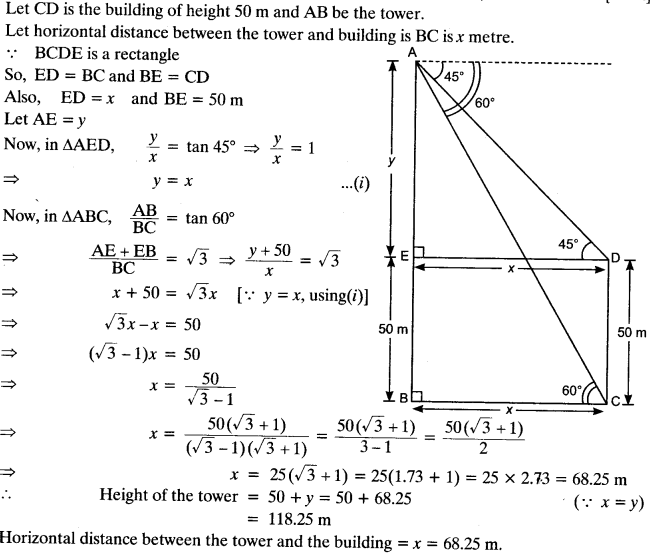
Areas Related to Circles Class 10 Important Questions | NCERT Maths Chapter-12
Areas Related to Circles Class 10 Important Questions
The start of class 10 marks the beginning of the foundation for class 11 and class 12. It is very important study the basics in order to understand each and every chapter properly. In this page, we have provided all the important question for cbse class 9 that could be asked in the examination. Students also need to study the ncert solutions for class 10 in order to gain more knowledge and understanding the lessons. Questions and Answers are way to learn the new things in a proper way. NCERT textbooks downloads for class 9 in pdf are also available for the students if they need more help. By downloading these books, they can study from it. Our experts also prepared revision notes for class 9 so that students should see the details of each and every chapters. Class 9 important questions are the best to revise all the chapters in the best way.
Question 1.
In figure, ABCD is a square of side 14 cm. Semi-circles are drawn with each side of square as diameter. Find the area of the shaded region.
Solution:
Area of the square ABCD = 14 x 14 = 196 cm²
Area of semicircle AOB=1/2 x πr²
=1/2×22/7x7x7
Similarly, area of semicircle DOC = 77 cm²
Hence, the area of shaded region (Part W and Part Y) = Area of square -Area of two semicircles AOB and COD
= 196 – 154 = 42 cm²
Therefore, area of four shaded parts (i.e. X, Y, W, Z) = (2 x 42) cm² = 84 cm²
Question 2.
In figure, are shown two arcs PAQ and PBQ. Arc PAQ is a part of circle with centre O and radius OP while arc PBQ is a semicircle drawn on PQ as diameter with centre M. If OP = PQ = 10 cm, show that area of shaded region is
25(√3- π /6)cm²
Solution:
OP = OQ = 10 cm
PQ = 10 cm
So, ΔOPQ is an equilateral triangle
∠POQ = 60°
Area of segment PAQM = Area of sector OPAQ – Area of ΔOPQ
=60/360 x π x 10 x 10-√3/4 x 10 x 10
=(100π/6-100√3/4)cm²
Area of semicircle =1/2 x π x 5 x 5 = 25/2π cm²
Area of the shaded region =25/2π-(100π/6-100√3/4)=25π/2-50π/3+25√3
=75π-100π/6+25√3=25√3-25π/6
=25(√3-π/6)cm²
Question 3.
In figure, O is the centre of a circle such that diameter AB = 13 cm and AC = 12 cm. BC is joined. Find the area of the shaded region.
Solution:
Here, BC² = AB²-AC²
= 169-144 = 25 BC = 5
Area of shaded region = Area of semicircle – Area of right triangle ABC
=1/2 x πr²-1/2AC x BC
=1/2 x 3.14(13/2)²-1/2 x 12 x 5
=66.33 – 30 = 36.33 cm²
Question 4.
In figure, find the area of the shaded region, enclosed between two concentric circles of radii 7 cm and 14 cm where∠AOC = 40°.
Solution:
Area of shaded region=360°-θ/360° x π(R²-r²)
=320°/360° x π[(14)²-(7)²]
=8/9 x 22/7(196-49)=8/9 x 22/7 x 147
=1232/3=410.67 cm²
Question 5.
Find the area of shaded region in figure, where a circle of radius 6 cm has been drawn with vertex O of an equilateral triangle OAB of side 12 cm
Solution:
Area of ΔOAB=√3/4(side)²=√3/4 x (12)²
=36√3=36 x 1.73
=62.28 cm²
area of circle with center O =πr²=3.14 x (6)²
=3.14 x 36 =113.04 cm²
area of sector(OLQP)=πr² x θ/360°=3.14 x 6² x 60°/360°
=3.14 x 36 x 1/6 =18.84 cm²
area of shaded region=area of ΔOAB+area of circle-2 area of sector OLQP
=(62.28+113.04-2 x 18.84)cm²
=137.64cm²
Question 6.
In figure, is a chord AB of a circle, with centre O and radius 10 cm, that subtends a right angle at the centre of the circle. Find the area of the minor segment AQBP. Hence, find the area of major segment ALBQA
Solution:
Area of minor segment APBQ=θ/360° x πr²-r²sin45°cos45°
=3.14 x 100/4-100 x 1/√2 x 1/√2
=(78.5-50)cm²=28.5 cm²
Area of major segment ALBQA =πr²-area of minor segment
=3.14 x (10)²-28.5
=(314-28.5)cm²=285.5 cm²
Long Answer Type Questions [4 Marks]
Question 7.
An elastic belt is placed around the rim of a pulley of radius 5 cm. From one point C on the belt, the elastic belt is pulled directly away from the centre O of the pulley until it is at P, 10 cm from the point O. Find the length of the belt that is still in contact with the pulley.Also find the shaded area, (use π = 3.14 and √3 = 1.73)
Solution:


Question 8.
In figure, is shown a sector OAP of a circle with centre O, containing Z0. AB is perpendicular to the radius OA and meets OP produced at B. Prove that the perimeter of shaded region is r[tanθ+secθ+πθ/180-1]
Solution:

Question 9.
Find the area of the shaded region in figure, where APD, AQB, BRC and CSD are semi-circles of diameter
14 cm, 3.5 cm, 7 cm and 3.5 cm respectively
Solution:
Area of shaded region
= Area of semicircle APD + Area of semicircle BRC – 2 x Area of semicircle AQB

2015
Short Answer Type Questions II [3 Marks
Question 10.
In figure, APB and AQO are semicircle, and AO = OB. If the perimeter of the figure is 40 cm, find the area of the shaded region.
Solution:
Let r be the radius of the semicircle APB, i.e. OB = OA = r, then r/2 is the radius of the semicircle AQO.
Question 11.
In figure, find the area of the shaded region
Solution:
Question 12.
Find the area of the minor segment of a circle of radius 14 cm, when its central angle is 60°. Also find the area of the corresponding major segment
Solution:
Question 13.
All the vertices of a rhombus lie on a circle.Find the area of rhombus,if the area of circle is 1256 cm²
Solution:
Question 14.
The long and short hand of a clock are 6cm and 4 cm long respectively,Find the sum of the distance travelled by their tips in 24hrs.
Solution:
Question 15.

Solution:
















 pt>
pt>