Ex 6.5 Class 12 Maths Question 1.
Find the maximum and minimum values, if any, of the following functions given by
(i) f(x) = (2x – 1)² + 3
(ii) f(x) = 9x² + 12x + 2
(iii) f(x) = – (x – 1)² + 10
(iv) g(x) = x3 + 1
Solution:
(i) Minimum value of (2x – 1)² is zero.
Minimum value of (2x – 1)² + 3 is 3
Clearly it does not have maximum value,
(ii) f(x) = 9x² + 12x + 2
⇒ f(x) = (3x + 2)² – 2
Minimum value of (3 + 2)² is zero.
∴ Min.value of (3x + 2)² – 2 = 9x² + 12x + 2 is – 2
f (x) does not have finite maximum value
(iii) f(x) = – (x – 1)² + 10
Maximum value of – (x – 1)² is zero
Maximum valuer f f(x) = – (x – 1)² + 10 is 10
f (x) does not have finite minimum value.
(iv) As x—»∞,g(x)—»∞;Also x—»-∞,g(x)—»-∞
Thus there is no maximum or minimum value of f(x)
Ex 6.5 Class 12 Maths Question 2.
Find the maximum and minimum values, if any, of the following functions given by
(i) f(x) = |x + 2| – 1
(ii) g(x) = -|x + 1| + 3
(iii) h (x) = sin 2x + 5
(iv) f(x) = |sin(4x + 3)|
(v) h(x) = x + 1,x∈(-1,1)
Solution:
(i) We have :f(x) = |x + 2 |-1 ∀x∈R
Now |x + 2|≥0∀x∈R
|x + 2| – 1 ≥ – 1 ∀x∈R ,
So -1 is the min. value of f(x)
now f(x) = -1
⇒ |x + 2|-1
⇒ |x + 2| = 0
⇒ x = – 2
(ii) We have g(x) = -|x + 1| + 3 ∀x∈R
Now | x + 1| ≥ 0 ∀x∈R
-|x+ 1| + 3 ≤3 ∀x∈R
So 3 is the minimum value of f(x).
Now f(x) = 3
⇒ -|x+1| + 3
⇒ |x+1| = 0
⇒ x = – 1.
(iii) Thus maximum value of f(x) is 6 and minimum value is 4.
(iv) Let f(x) = |sin4x + 3|
Maximum value of sin 4x is 1
∴ Maximum value of |sin(4x+3)| is |1+3| = 4
Minimum value of sin 4x is -1
∴ Minimum value of f(x) is |-1+3| = |2|= 2
(v) Greatest value of f (x) is 2 and least value is 0.
Ex 6.5 Class 12 Maths Question 3.
Find the local maxima and local minima, if any, of the following functions. Find also the local maximum and the local minimum values, as the case may be:
(i) f(x) = x2
(ii) g(x) = x3 – 3x
(iii) h(x) = sinx+cosx,0<x<
(iv) f(x) = sin4x + cos4x,0<x<
(v) f(x) = x3 – 6x2 + 9x:+15
(vi) g(x) =  , x>0
, x>0
(vii) g(x) =  , x>0
, x>0
(viii) f(x) =  , x>0
, x>0
Solution:
(i) Let f(x) = x² ⇒ f’(x) = 2x
Now f'(x) = 0 ⇒ 2x = 0 i.e., x = 0
At x = 0; When x is slightly < 0, f’ (x) is -ve When x is slightly > 0, f(x) is +ve
∴ f(x) changes sign from -ve to +ve as x increases through 0.
⇒ f’ (x) has a local minimum at x = 0 local minimum value f(0) = 0.






Ex 6.5 Class 12 Maths Question 4.
Prove that the following functions do not have maxima or minima:
(i) f(x) = ex
(ii) f(x) = log x
(iii) h(x) = x3 + x2 + x + 1
Solution:
(i) f'(x) = ex;
Since f’ (x) ≠ 0 for any value of x.
So f(x) = ex does not have a max. or min.
(ii) f’ (x) = 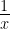 ; Clearly f’ (x) ≠ 0 for any value of x.
; Clearly f’ (x) ≠ 0 for any value of x.
So,f’ (x) = log x does not have a maximum or a minimum.
(iii) We have f(x) = x3 + x2 + x + 1
⇒f’ (x) = 3x2 + 2x + 1
Now, f’ (x) = 0 => 3x2 + 2x + 1 = 0

i.e. f'(x) = 0 at imaginary points
i.e. f'(x) ≠ 0 for any real value of x
Hence, there is neither max. nor min.
Ex 6.5 Class 12 Maths Question 5.
Find the absolute maximum value and the absolute minimum value of the following functions in the given intervals:
(i) f(x) = x3, x∈ [-2,2]
(ii) f(x) = sin x + cos x, x ∈ [0, π]
(iii) f(x) = ![4x-\frac { 1 }{ 2 } { x }^{ 2 },x\in \left[ -2,\frac { 9 }{ 2 } \right] 4x-\frac { 1 }{ 2 } { x }^{ 2 },x\in \left[ -2,\frac { 9 }{ 2 } \right]](https://s0.wp.com/latex.php?latex=4x-%5Cfrac+%7B+1+%7D%7B+2+%7D+%7B+x+%7D%5E%7B+2+%7D%2Cx%5Cin+%5Cleft%5B+-2%2C%5Cfrac+%7B+9+%7D%7B+2+%7D+%5Cright%5D+&bg=ffffff&fg=000&s=2)
(iv) f(x) = ![{ (x-1) }^{ 2 }+3,x\in \left[ -3,1 \right] { (x-1) }^{ 2 }+3,x\in \left[ -3,1 \right]](https://s0.wp.com/latex.php?latex=%7B+%28x-1%29+%7D%5E%7B+2+%7D%2B3%2Cx%5Cin+%5Cleft%5B+-3%2C1+%5Cright%5D+&bg=ffffff&fg=000&s=2)
Solution:
(i) We have f’ (x) = x3 in [ -2,2]
∴ f'(x) = 3x²; Now, f’ (x) = 0 at x = 0, f(0) = 0
Now, f(-2) = (-2)3 = – 8; f(0) = (0)² = 0 and f(0) = (2) = 8
Hence, the absolute maximum value of f (x) is 8 which it attained at x = 2 and absolute minimum value of f(x) = – 8 which is attained at x = -2.
(ii) We have f (x) = sin x + cos x in [0, π]
f’ (x) = cos x – sin x for extreme values f’ (x) = 0

Ex 6.5 Class 12 Maths Question 6.
Find the maximum profit that a company can make, if the profit function is given by p(x) = 41 – 24x – 18x²
Solution:
Profit function in p(x) = 41 – 24x – 18x²
∴ p'(x) = – 24 – 36x = – 12(2 + 3x)
for maxima and minima, p'(x) = 0
Now, p'(x) = 0
⇒ – 12(2 + 3x) = 0
⇒ x =  ,
,
p'(x) changes sign from +ve to -ve.
⇒ p (x) has maximum value at x = 
Maximum Profit = 41 + 16 – 8 = 49.
Ex 6.5 Class 12 Maths Question 7.
Find both the maximum value and the minimum value of 3x4 – 8x3 + 12x2 – 48x + 25 on the interval [0,3].
Solution:
Let f(x) = 3x4 – 8x3 + 12x2 – 48x + 25
∴f'(x) = 12x3 – 24x2 + 24x – 48
= 12(x2 + 2)(x – 2)
For maxima and minima, f'(x) = 0
⇒ 12(x2 + 2)(x – 2) = 0
⇒ x = 2
Now, we find f (x) at x = 0,2 and 3, f (0) = 25,
f (2) = 3 (24) – 8 (23) + 12 (22) – 48 (2) + 25 = – 39
and f (3) = (34) – 8 (33) + 12 (32) – 48 (3) + 25
= 243 – 216 + 108 – 144 + 25 = 16
Hence at x = 0, Maximum value = 25
at x = 2, Minimum value = – 39.
Ex 6.5 Class 12 Maths Question 8.
At what points in the interval [0,2π], does the function sin 2x attain its maximum value?
Solution:
We have f (x) = sin 2x in [0,2π], f’ (x) = 2 cos 2 x
For maxima and minima f’ (x) = 0 => cos 2 x = 0

Ex 6.5 Class 12 Maths Question 9.
What is the maximum value of the function sin x + cos x?
Solution:
Consider the interval [0, 2π],
Let f(x) = sinx + cosx,
f’ (x) = cosx – sinx
For maxima and minima, f’ (x) = 0

Ex 6.5 Class 12 Maths Question 10.
Find the maximum value of 2x3 – 24x + 107 in the interval [1,3]. Find the maximum value of the same function in [-3, -1].
Solution:
∵ f(x) = 2x3 – 24x + 107
∴f(x) = 6x2 – 24 ,
For maxima and minima f'(x) = 0;⇒ x = ±2
For the interval [ 1,3], we find the values of f (x)
at x = 1,2,3; f(1) = 85, f(2) = 75, f(3) = 89
Hence, maximum f (x) = 89 at x = 3
For the interval [-3, -1], we find the values of f(x) at x = – 3, – 2, – 1;
f(-3) = 125;
f(-2) = 139
f(-1) = 129
∴ max.f(x) = 139 at x = – 2.
Ex 6.5 Class 12 Maths Question 11.
It is given that at x = 1, the function x4 – 62x2 + ax + 9 attains its maximum value, on the interval [0,2]. Find the value of a.
Solution:
∵ f(x) = x4 – 62x2 + ax + 9
∴ f’ (x) = 4x3 – 124x + a
Now f’ (x) = 0 at x = 1
⇒ 4 – 124 + a = 0
⇒ a = 120
Now f” (x) = 12x2 – 124:
At x = 1 f” (1) = 12 – 124 = – 112 < 0
⇒ f(x) has a maximum at x = 1 when a = 120.
Ex 6.5 Class 12 Maths Question 12.
Find the maximum and minimum values of x + sin 2x on [0,2π]
Solution:
∴f(x) = x + sin2x on[0,2π]
∴f’ (x) = 1+2 cos2x
For maxima and minima f’ (x) = 0

Ex 6.5 Class 12 Maths Question 13.
Find two numbers whose sum is 24 and whose product is as large as possible.
Solution:
Let the required numbers hex and (24-x)
∴Their product,p = x(24 – x) = 24x – x²
Now  = 0 ⇒24 – 2x = 0 ⇒ x = 12
= 0 ⇒24 – 2x = 0 ⇒ x = 12
Also  = -2<0: ⇒ p is max at x = 12
= -2<0: ⇒ p is max at x = 12
Hence, the required numbers are 12 and (24-12)i.e. 12.
Ex 6.5 Class 12 Maths Question 14.
Find two positive numbers x and y such that x + y = 60 and xy3 is maximum.
Solution:
We have x + y = 60
⇒ y = 60 – x …(i)

Hence, the req. numbers are 15 and (60 -15) i.e. 15 and 45.
Ex 6.5 Class 12 Maths Question 15.
Find two positive numbers x and y such that their sum is 35 and the product x2 y5 is a maximum.
Solution:
We have x + y = 35 ⇒ y = 35 – x
Product p = x2 y5
= x2 (35 – x)5

Ex 6.5 Class 12 Maths Question 16.
Find two positive numbers whose sum is 16 and the sum of whose cubes is minimum.
Solution:
Let two numbers be x and 16 – x

Hence, the required numbers are 8 and (16-8) i.e. 8 and 8.
Ex 6.5 Class 12 Maths Question 17.
A square piece of tin of side 18 cm is to be made into a box without top, by cutting a square from each corner and folding up the flaps to form the box. What should be the side of the square to be cut off so that the volume of the box is the maximum possible.
Solution:
Let each side of the square to be cut off be x cm.
∴ for the box length = 18 – 2x: breadth = 18 – 2x and height = x

Ex 6.5 Class 12 Maths Question 18.
A rectangular sheet of tin 45 cm by 24 cm is to be made into a box without top, by cutting off square from each comer and folding up the flaps. What should be the side of the square to be cut off so that the volume of the box is maximum?
Solution:
Let each side of the square cut off from each comer be x cm.
∴ Sides of the rectangular box are (45 – 2x), (24 – 2x) and x cm.

Ex 6.5 Class 12 Maths Question 19.
Show that of all the rectangles inscribed in a given fixed circle, the square has the maximum area.
Solution:
Let the length and breadth of the rectangle inscribed in a circle of radius a be x and y respectively.
∴ x² + y² = (2a)² => x² + y² = 4a² …(i)
∴ Perimeter = 2 (x + y)

Ex 6.5 Class 12 Maths Question 20.
Show that the right circular cylinder of given surface and maximum volume is such that its height is equal to the diameter of the base.
Solution:
Let S be the given surface area of the closed cylinder whose radius is r and height h let v be the its Volume. Then

Ex 6.5 Class 12 Maths Question 21.
Of all the closed cylindrical cans (right circular), of a given volume of 100 cubic centimeters, find the dimensions of the can which has the minimum surface area ?
Solution:
Let r be the radius and h be the height of cylindrical can.

Ex 6.5 Class 12 Maths Question 22.
A wire of length 28 m is to be cut into two pieces. One of the pieces is to be made into a square and the other into a circle. What should be the length of the two pieces so that the combined area of the square and the circle is minimum ?
Solution:
Let one part be of length x, then the other part = 28 – x
Let the part of the length x be converted into a circle of radius r.


Ex 6.5 Class 12 Maths Question 23.
Prove that the volume of the largest cone that can be inscribed in a sphere of radius R is 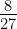 of the volume of the sphere.
of the volume of the sphere.
Solution:
Let a cone. VAB of greatest volume be inscribed in the sphere let AOC = θ
∴ AC, radius of the base of the cone = R sin θ
and VC = VO + OC = R(1 +cosθ)
= R + Rcosθ
= height of the cone.,
V, the volume of the cone.


Ex 6.5 Class 12 Maths Question 24.
Show that die right circular cone of least curved surface and given volume has an altitude equal to √2 time the radius of the base.
Solution:
Let r and h be the radius and height of the cone.

Ex 6.5 Class 12 Maths Question 25.
Show that the semi-vertical angle of the cone of the maximum volume and of given slant height is tan-1 √2.
Solution:
Let v be the volume, l be the slant height and 0 be the semi vertical angle of a cone.

Ex 6.5 Class 12 Maths Question 26.
Show that semi-vertical angle of right circular cone of given surface area and maximum volume is 
Solution:
Let r be radius, l be the slant height and h be the height of the cone of given surface area s.Then


Choose the correct answer in the Exercises 27 and 29.
Ex 6.5 Class 12 Maths Question 27.
The point on die curve x² = 2y which is nearest to the point (0,5) is
(a) (2 √2,4)
(b) (2 √2,0)
(c) (0,0)
(d) (2,2)
Solution:
(a) Let P (x, y) be a point on the curve The other point is A (0,5)
Z = PA² = x² + y² + 25 – 10y [∵ x² = 2y]

Ex 6.5 Class 12 Maths Question 28.
For all real values of x, the minimum value of 
(a) 0
(b) 1
(c) 3
(d) 
Solution:
(d) Let 

Ex 6.5 Class 12 Maths Question 29.
The maximum value of ![{ \left[ x\left( x-1 \right) +1 \right] }^{ \frac { 1 }{ 3 } },0\le x\le 1 { \left[ x\left( x-1 \right) +1 \right] }^{ \frac { 1 }{ 3 } },0\le x\le 1](https://s0.wp.com/latex.php?latex=%7B+%5Cleft%5B+x%5Cleft%28+x-1+%5Cright%29+%2B1+%5Cright%5D+%7D%5E%7B+%5Cfrac+%7B+1+%7D%7B+3+%7D+%7D%2C0%5Cle+x%5Cle+1&bg=ffffff&fg=000&s=2) is
is
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 1
(d) 0
Solution:
(c) Let y = ![{ \left[ x\left( x-1 \right) +1 \right] }^{ \frac { 1 }{ 3 } },0\le x\le 1 { \left[ x\left( x-1 \right) +1 \right] }^{ \frac { 1 }{ 3 } },0\le x\le 1](https://s0.wp.com/latex.php?latex=%7B+%5Cleft%5B+x%5Cleft%28+x-1+%5Cright%29+%2B1+%5Cright%5D+%7D%5E%7B+%5Cfrac+%7B+1+%7D%7B+3+%7D+%7D%2C0%5Cle+x%5Cle+1&bg=ffffff&fg=000&s=2)
































































































































































































































































































